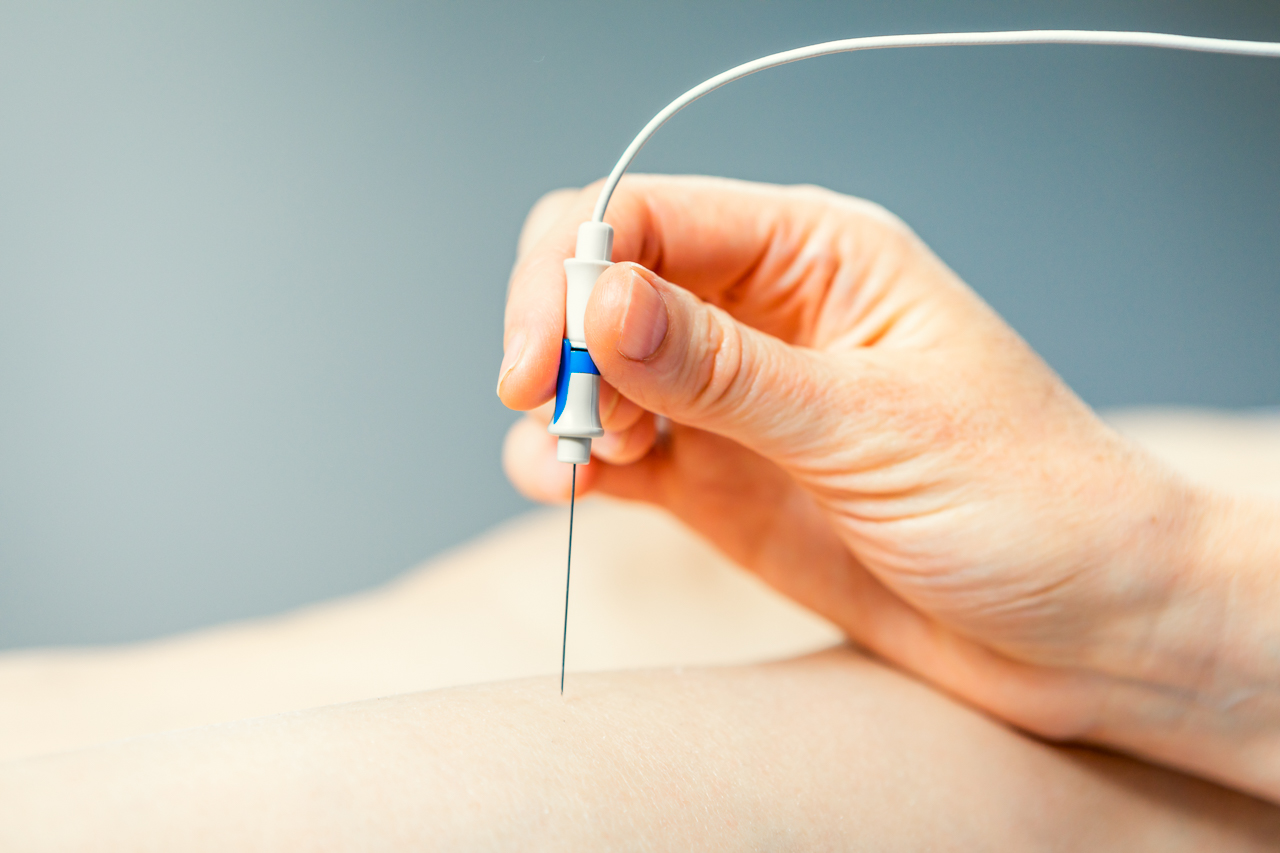
1. NERVE ULTRASOUND


With technology advances it has has rapidly developed into becoming a more precise tool. Even small nerves of 1mm in diameter or less can be observed with state oft he art technic. Moreover, the test is safe and painless and does not expose your body to radiation. By using nerve ultrasound, a dynamic, real-time examination can be achieved.
It is especially helpful for diagnosing nerve compression syndromes (“pinched nerves”), such as carpal tunnel syndrome, ulnar neuropathy at the elbow, and peroneal (fibular) neuropathy at the fibular head. Using neuromuscular ultrasound, we can detect inflammation, trauma, or tumors of the nerves and muscles.
In parallel to its diagnostic use, interventional applications of neuromuscular ultrasound have quickly advanced. Ultrasound has a high value in guiding injections. It helps to choose the path between the skin and the target structure that is the safest, shortest, and easiest.
Thus, nerve ultrasound can guide administration of medication to nerves in pain medicine (ultrasound guided nerve blocks). Due to its high resolution and precise guiding of the needle, it improves safety margins. Ultrasound helps to identify structures that should be avoided during injections, such as vessels, tendons, and nerves.
Muscle ultrasound can guide the therapeutic injections of botulinum toxin in muscle. Ursing ultrasound, we can administer botulinum toxin injections in precise locations.
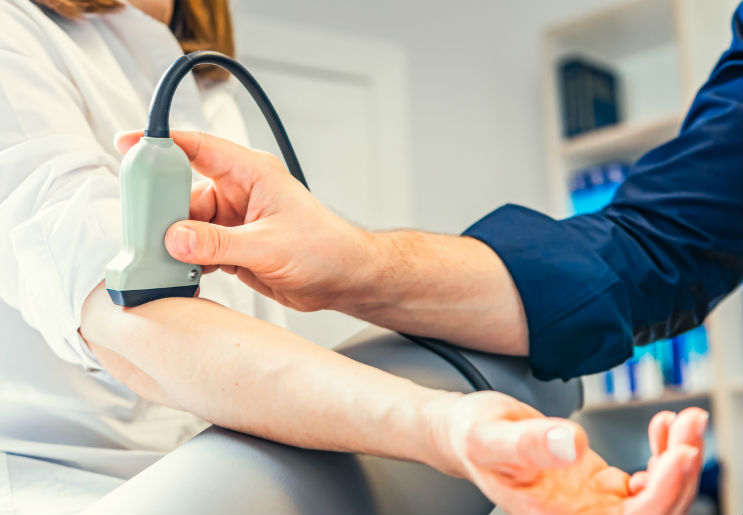
2. ULTRASOUND BRAIN SUPPLYING ARTERIES


Carotid and Transcranial ultrasound (Duplex/Doppler) Studies
Carotid and transcranial ultrasound studies most often are performed to assess a person’s risk of having a stroke of transient ischemic attack (TIA or “mini-stroke”). It gives important information to manage treatment in patients at risk for these issues.
Ultrasound studies are very useful in helping many patients reduce their risks for strokes and “mini-strokes” (so called transient ischemic attacks, TIA’s). We offer state-of-the-art carotid and transcranial ultrasound studies for accurate diagnoses and treatment management
When is a ultrasound study of the brain supplying arteries recommended:
-In case of cardiovascular risk factors, such as
- high blood pressure (arterial hypertension)
- high cholesterol, elevated blood levels
- a history of smoking
- coronary artery disease or other vascular disease
- diabetes mellitus
– In case of a personal (or family) history of strokes or TIAs
3. NEUROLOGICAL TESTING – VEP, BAER, SSER, EEG
- Visual evoked potentials (VEP)
A VEP test helps to evaluate function oft the optic nerve. This helps to diagnose or assess problems with vision. During the test, electrodes are attached to the occiput to measure the brains electrical activity, while the patient will be asked to focus on images on a screen located in a small distance. - Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER)
This test is used mainly to evaluate symptoms related to hearing and balance. A series of clicking noises are transmitted to headphones. Using electrodes attached to the skin, brain activity is evaluated as the sounds occur. - Somatosensory evoked response (SSER)
These tests are used to evaluate processes affecting the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system. During the test, electrodes are placed on the skin of the head, while the nerve to be tested is situmllated with small electric impulses. Different nerves oft he body within the face, arms and legs can be studied using SSER. - Electroencephalogram (EEG)
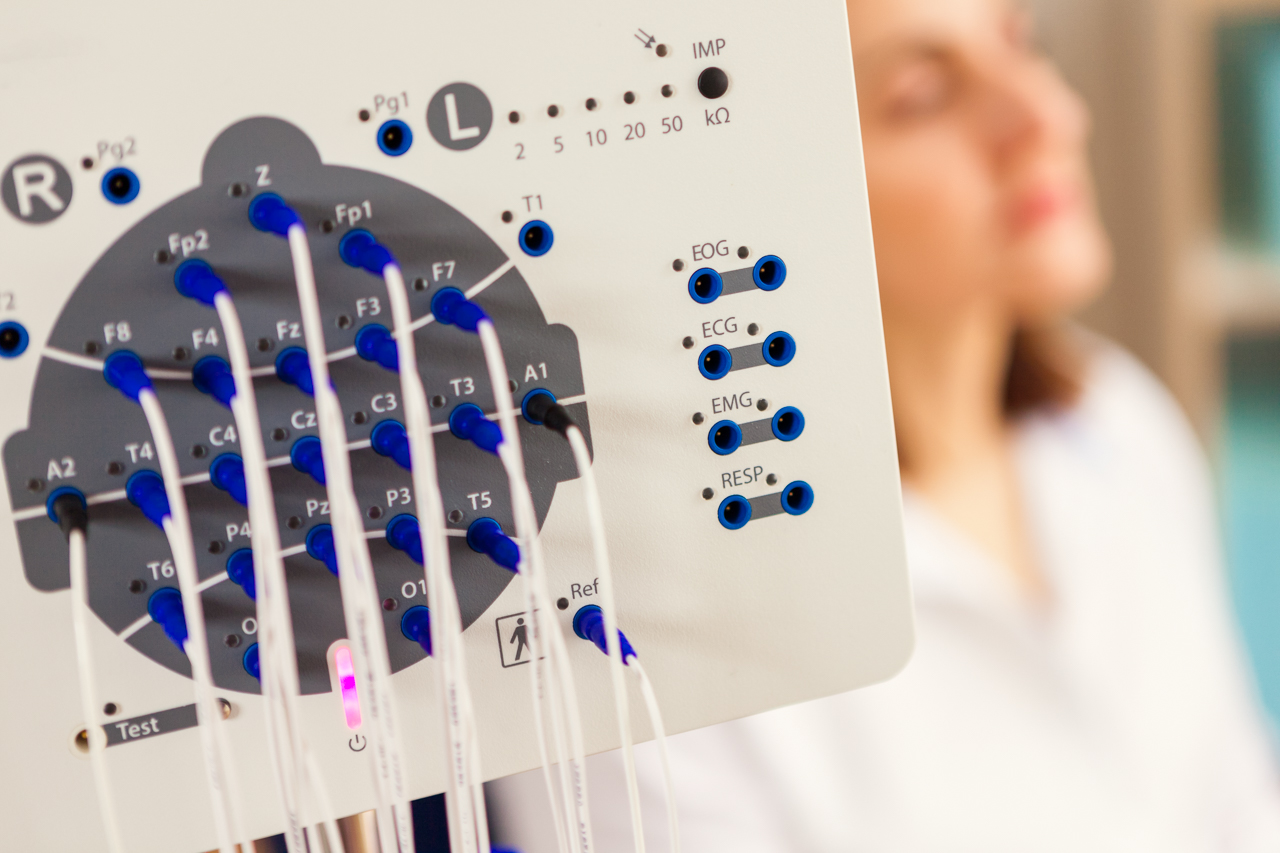
With EEG the electrical activity in the brain can be measured. First, small small discs (electrodes) are placed externally on the scalp. With help of these electrodes, electrical impulses in the brain will be transmitted via wires to a machine and a graph depicting the activity (brain waves) is created. Normal brain waves have a particular rhythm and shape. Abnormal brain waves can suggest an underlying seizure disorder or other neurological conditions. EEGs are used to diagnose a wide array of issues related to the brain, diagnostic workup of syncope and fits, epilepsy and other seizure disorders, brain tumors, encephalopathy (brain dysfunction), encephalitis (brain inflammation), stroke, dementia, brain injury etc.
Here you can make an appointment for a diagnostic.
Do not hesitate to contact us.
Phone 030 23 54 55 45