Neurology is a specialty practice of medicine that focuses on disorders of the brain, spinal cord, muscles and peripheral nerves.
Special interests are in neuromuscular diseases, that is disorders of the peripheral nerves and muscles.
One of our therapeutic principles is: whenever possible, we try to treat conditions without using prescription medications. We are working with selective integrative medicine approaches that have stood the test of time. When medications are needed, we start using the lowest dose and fewest number of medications possible. If needed, the full range of neurological modern therapies, including intravenous administration of medications can be provided.
Although a serious doctor would not guarantee 100% pain relief, as a matter of fact, most patients can be helped with an appropriate individual treatment.
First step towards an effective therapy is an accurate diagnosis. A thorough history will be taken of all your symptoms and associated factors. In the next step, appropriate tests will be done (ultrasound of brain supplying arteries, brain imaging, etc), depending on your symptoms.
The individual therapy goals and preferences will be discussed.
Fortunately, today, various treatment modalities are available. These include non-pharmcological approaches (usually the first step), pharmacological medications, various injections, most often trigger-point-injections or nerve blocks. Botox-Injection is a relatively new therapy option for chronic migraine.
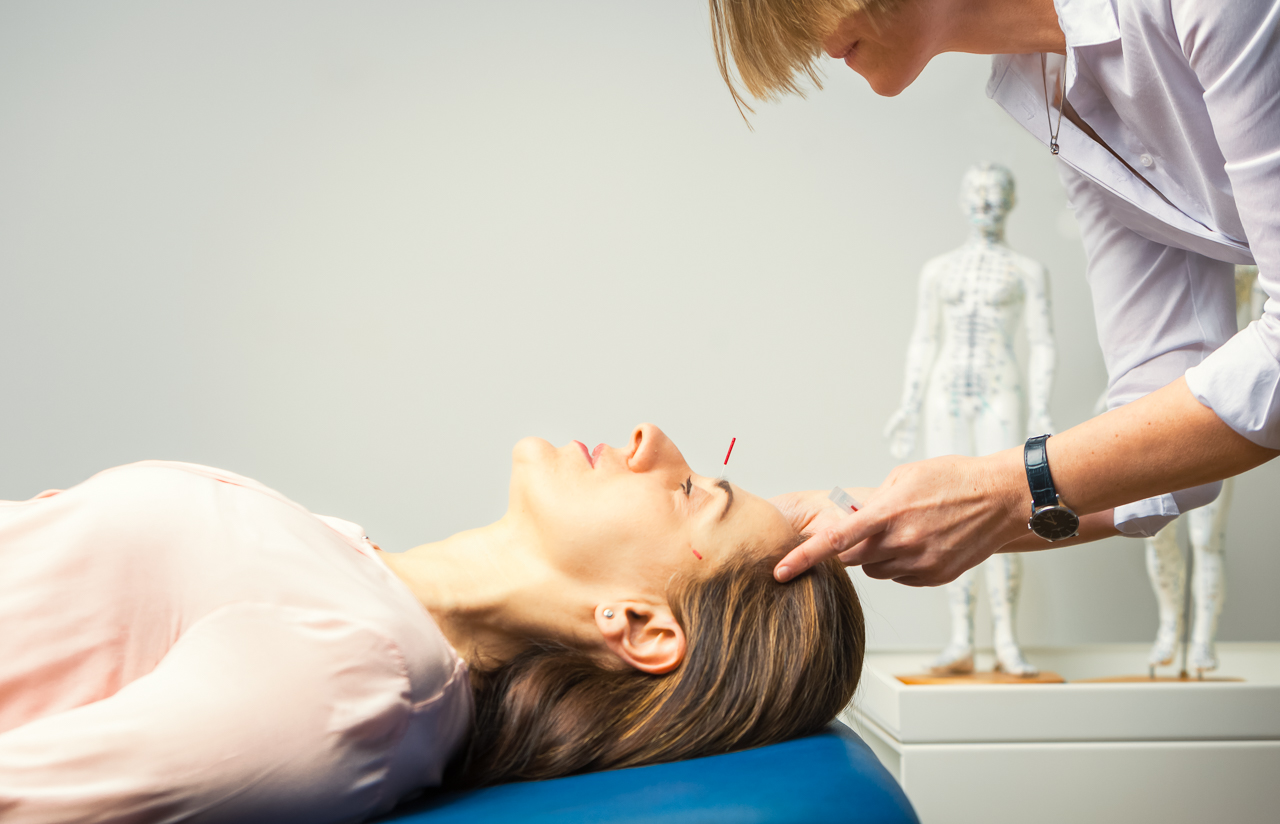
Another key component of our concept is to offer advanced complementary care, such as neural therapy and accupuncture

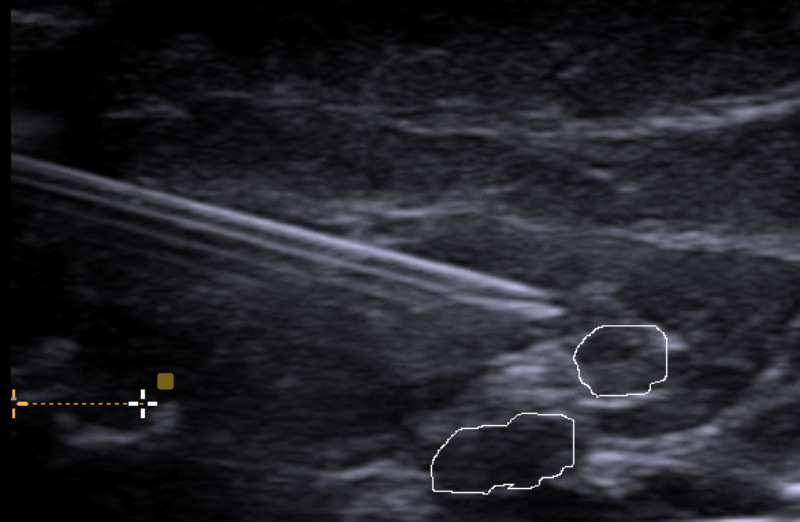
Our approach is to combine this with use of nerve ultrasound. Ultrasound allows real-time imaging of the positions of the targeted nerve and surrounding arteries or veins, as well as the advancing needle. Ultrasound guidance of injections thus helps to improve the accuracy of the procedure, increase the success rate, and may reduce the risk of complications.
There are different kinds of nerve blocks used for various purposes.
- Diagnostic nerve blocks
By using a diagnostic nerve block, the aim is to find out, whether pain or sensory disturbances are caused by a certain nerve. Here a high accuracy in targeting the oftentimes very small (1mm) nerves can be achieved by injection guidance with nerve ultrasound. If the origin of pain is confirmed, then an exact therapy can be planned
- Therapeutic nerve blocks
If the origin of pain (or other symptoms) is attributed to a certain nerve, therapeutic injections can be performed. Here we are using ultrasound guidance to target the nerve specifically and avoid complications of injections. Different medications can be used to inject, depending on the individual situation.
- Prognostic nerve blocks
A nerve block can be used to predict treatment repsonse. If a nerve block relieves pain, this is an important information to decide, wether more permanent treatments (such as surgery) would be successful.
Thus, ultrasound guided perineurial injections can help with pain control and improve function and quality of life. Therapeutic goals with which nerve block can help are different in every individual – it might be to control pain, or to help avoid surgery, or to be able to take a more active role in physical therapy, to have a sound basis to plan specific nerve surgery …
It comprises an array of different technical procedures. Some of the most important procedures are widely used internationally under different names, such as nerve blocks, regional anaesthesia, trigger-point injections, etc. We combine this with ultrasound guidance of injections in „difficult places“. Thus neural therapy offers a low-risk and cortisone-free therapeutic approach.
It is believed to act through normalizing the illness-related dysfunction of the (autonomic) nervous system. Thus it is a branch of regulatory medicine. On the other hand is not really “alternative”, as many approaches are used in interventional pain medicine, when individuals nerves are treated. It is not a 100% clear yet, whether the injection of the sensory nerve brings about the therapeutic effect, or whether it is the effect on the network of autonomic (sympathetic) fibers which accompanies nerve.
What we like about neural therapy, that it is very pragmatic: it usually takes only 1-2 treatments to make clear, if it helps for your individual problem and you feel you want to proceed with this.
Segmental Therapy
One special approach in neural therapy is an indirect technique, referred to as “segmental therapy”. The anatomic basis for this approach is the segmental structure of the nervous system. Thereby the so-called cutaneovisceral reflex and the periosteovisceral reflex are used for therapy. By targeting an injection into the skin surface or periosteum of the same neurological segment in which the pain origin or the dysfunctional organ is located, a beneficial effect can be achieved. By the way, modern researchers argue, that the segmental structure of the nervous system is a „western scientific way“ to explain the therapeutic effect of many (but not all) acupuncture points.
Most people associate Botox with cosmetic treatments, but actually, Bottleinumtoxin first received FDA approval in the late 1980s as a treatment for eye spasms and strabismus (“crossed eyes”).
What is Botulinumtoxin and how does it work?
It is a neuromuscular agent that blocks signaltransmitting from nerves to muscles. This means, by controlling the nerves, Botox can control muscle contractions. This is of course not restricted to muscle contractions responsible for wrinkle formation, but also those associated with painful spasms or other neurological disorders.
Botox gets injected into different muscles. As a result of Botulinumtoxin treatment, injected muscles reduce their contraction resulting in reduction of painful muscle spasms.
Botox has become a standard treatment of an array of neurological conditions, including:
- Dystonia
- Cervical dystonia – that is muscle spasms in neck muscles resulting in pain and involuntary movements of the head/neck/shoulder.
- spastic muscle contractions, for instance after a stroke
- blepharospasm (uncontrollable blinking or squinting due to spasm of the muscle around the eye)
- hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating
Botox in pain management
- migraine headaches
- neuropathy (nerve pain) in the hands, feet, and legs
- it can be also used to relieve painful spasms in the neck and shoulders
How is Botox used to treat migraine headaches
Botulinumtoxin is a relatively new treatment, shown to be effective in chronic migraine. In this situation Botulinumtoxin injections are applied to muscles around the head and neck. This treatment has been shown to reduce the frequency of migraine headaches and to reduce the severity of symptoms when headaches do occur.


This can provide fast relief from acute pain conditions and headache.
Also we provide i.v. therapy for multiple sclerosis.
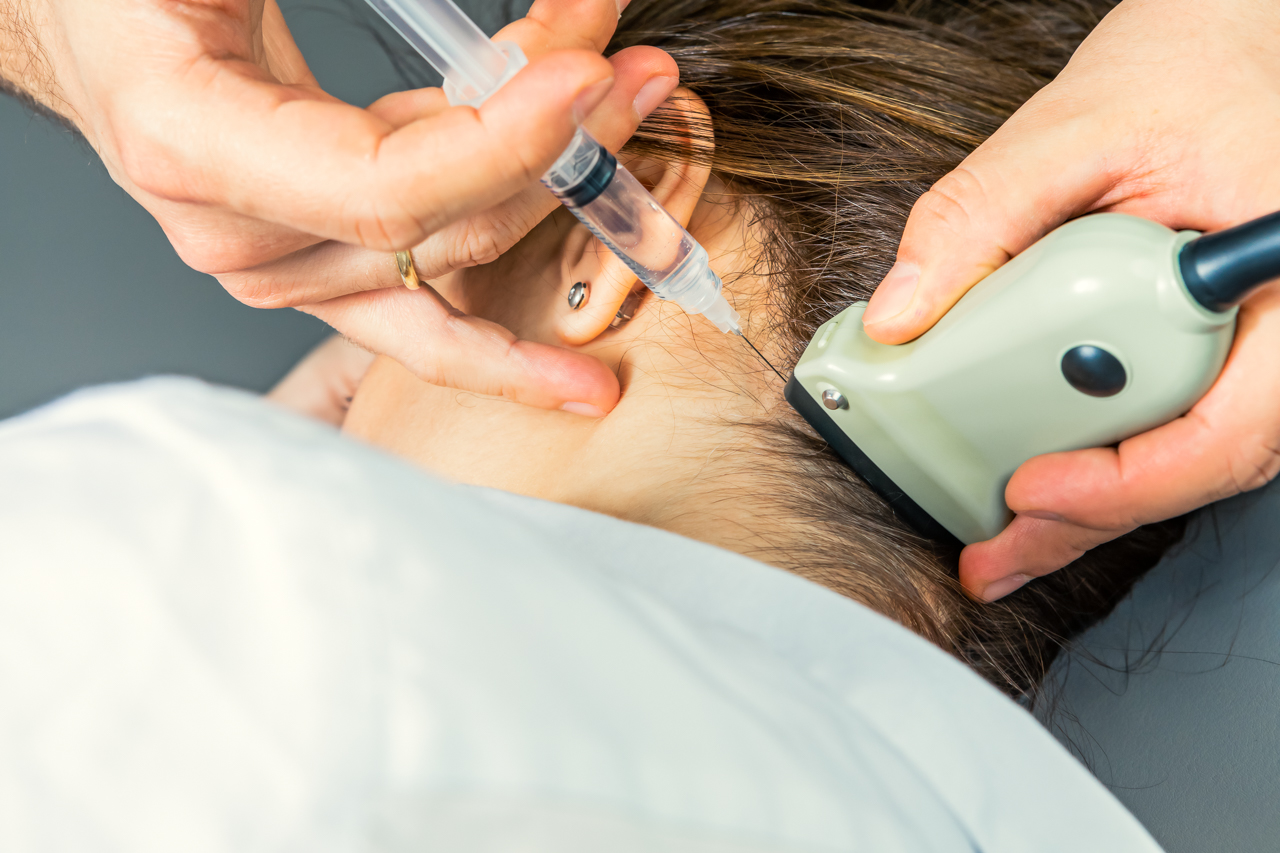

- Ultrasound-guided Perineural Injections and Nerve Blocks
- Ultrasound-guided Muscle-Injections, trigger-point therapy, myofascial pain.


Here you can make an appointment for a diagnostic.
Do not hesitate to contact us.
Phone 030 23 54 55 45


